
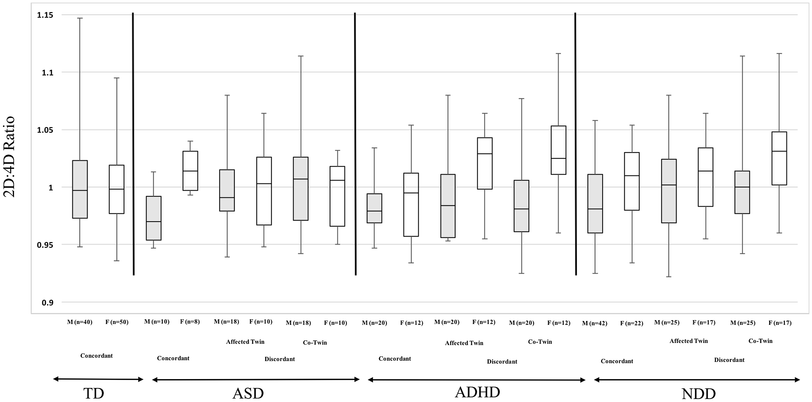
The authors have attempted to write a brief account on the digit ratios and the dimorphism observed in various physiological, psychological and behavioural traits. Slider with three articles shown per slide. Prenatal androgen exposure and therefore, digit ratios have been reported to be associated with numerical competencies, spatial skills, handedness, cognitive abilities, academic performance, sperm counts, personalities and prevalence of obesity, migraine, eating disorders, depression, myopia, autism etc. In this short report we explore the predictive nature of finger digit ratio (i.e., second/index finger length divided by fourth/ring finger length 2D:4D) and achievement. Our findings suggest that the 2D:4D ratio is not a relevant predictor of depression, while there was mixed evidence in the case of neuroticism. Usually, males have lower ratios when compared to females. Interestingly, it is constant since birth and not influenced by the adult hormone levels. Ratio of 2D:4D is found to correlate negatively to testosterone and positively to oestrogen in the foetus. These effects are sexually dimorphic, as females tend to have a higher 2D:4D ratio than males 17. Existing literature and recent research show accumulating evidence on 2D:4D ratio showing correlations with various phenotypic traits in humans. While a lower 2D:4D indicates a higher level of prenatal testosterone exposure, a higher ratio reflects a lower exposure to testosterone (ie, higher estrogen exposure) 10,1416.

One team in Scandinavia found that when hungry, people with lower 2D:4D ratios tend to make what was described as more "masculine food choices." And another team at Swansea University found that high income women tended to give birth to children with lower 2D:4D ratios.Digit ratios, especially 2D:4D ratio, a potential proxy marker for prenatal androgen exposure shows sexual dimorphism. This new finding comes on the heels of other factors attributed to the 2D:4D ratio.

They did not test whether the ratio was tied to exposure to testosterone in the womb but suggest it is a likely association, considering it has been shown to be the case in men. Put another way, they found that the longer a ring finger was relative to an index finger, the higher the grip strength. The researchers found what they describe as a "clear association" between lower 2D:4D ratios and grip strength. Each woman also had her hand grip strength measured using a dynamometer. The work by the researchers involved measuring ring and index finger length in 125 healthy women in Austria selected after factoring out age, environment, ethnicity and exercise as possible impactors of finger length. high prenatal testosterone), (v) all relationships between 2D:4D and MOB and day length were stronger for participants born in the first half of the 20th Century (19071955) in. Exposure to testosterone in the womb has been shown to play a role in this difference. That is, participants who were exposed to long days in their second and third foetal months tended to have low right 2D:4D and right 2D:4D < left 2D:4D (i.e. In some people, the ring finger is shorter than the index finger, while in others it is longer. Some studies showed a negative correlation between 2D:4D ratio and sports performances. The 2D:4D ratio is the ratio of finger length between the index and ring finger. Background Digit ratio (2D:4D) characterized by the length of the second digit (2D) divided by the length of the fourth digit (4D), is a powerful marker of athletic performance. In this new effort, the researchers found that the same is true for women. Prior research has shown that exposure to high levels of testosterone in the womb leads to human males born with a lower 2D:4D ratio and higher grip strength and overall heightened physical performance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
